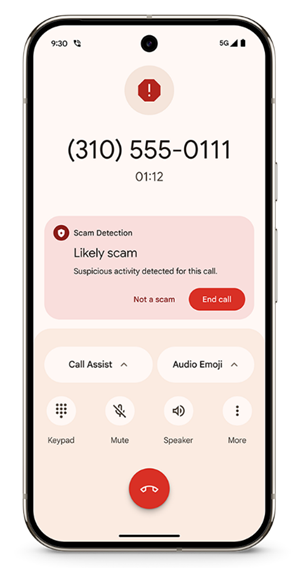
Google is introducing a new security feature in Android designed to prevent the unauthorized modification of critical system settings during phone calls. This measure is aimed at countering fraudulent schemes where cybercriminals manipulate victims into manually installing malicious applications.
While on a call, users will be restricted from enabling app installations from unknown sources or granting accessibility permissions to applications. Any attempt to alter these settings will trigger a warning notification, alerting the user to a potential scam and advising them to discontinue any suspicious actions.
This innovation is specifically designed to combat a deceptive attack technique known as Telephone-Oriented Attack Delivery (TOAD). In such schemes, attackers send fraudulent SMS messages urging victims to call a designated number, where they are then coerced into modifying device settings to facilitate malware installation.
The new feature is already available in the beta version of Android 16, which was released last week. It complements Google’s previous restrictions on granting sensitive permissions to manually installed applications.
Additionally, Google is continuously enhancing its threat prevention mechanisms. For instance, in high-risk cybercrime regions—including Brazil, India, Kenya, the Philippines, and others—Android automatically blocks the installation of suspicious APK files.
These proactive security measures are part of Google’s broader strategy to mitigate the risks of social engineering attacks and impose additional barriers to the spread of malware via phone calls. Through these initiatives, Google aims to fortify Android’s defenses against evolving cyber threats and protect users from deceptive tactics employed by cybercriminals.