GreyNoise specialists have issued a warning regarding the escalation of exploitation of a critical vulnerability in PHP-CGI, which initially affected primarily Japanese organizations. The attacks have now expanded across multiple regions, necessitating urgent defensive measures to mitigate the growing threat.
Recently, Cisco Talos reported the discovery of a malicious campaign targeting organizations in Japan. The attacks leveraged CVE-2024-4577, a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in PHP-CGI, assigned a CVSS score of 9.8.
Threat actors exploited vulnerable PHP-CGI installations on Windows systems to deploy Cobalt Strike and execute subsequent attacks using the TaoWu toolkit. Key attack characteristics included the use of HTTP POST requests with MD5 hashes as indicators of successful exploitation, deployment of malicious PowerShell scripts, and command-and-control (C2) infrastructure hosted on Alibaba Cloud.
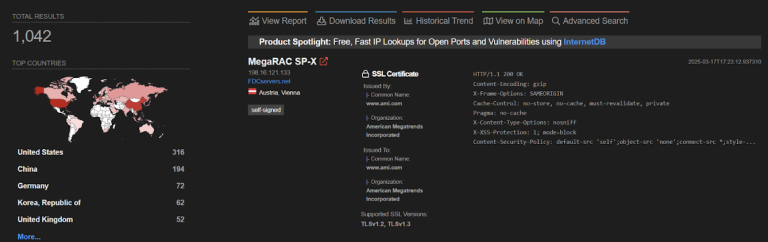
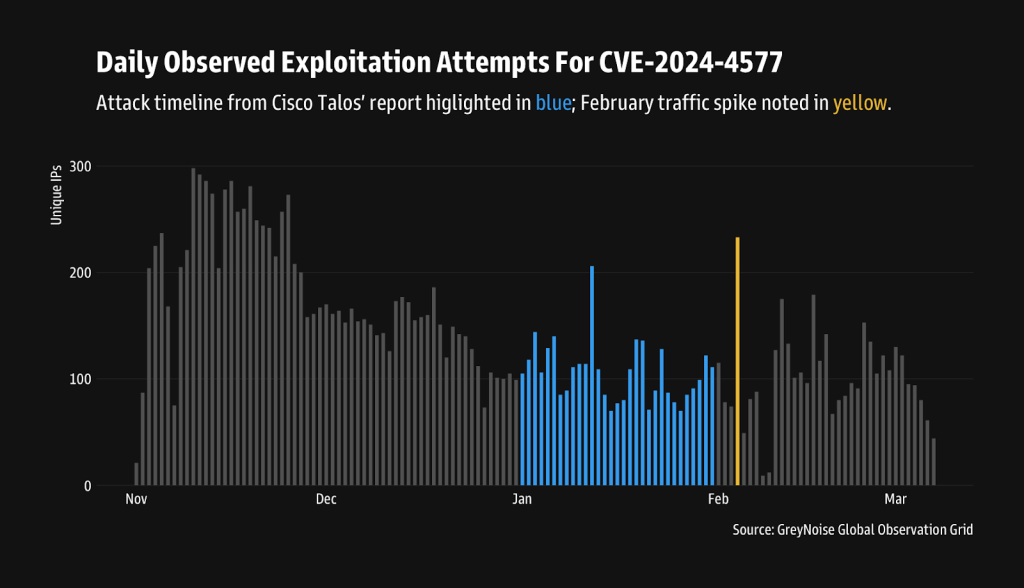
According to GreyNoise, the scale of the attacks is significantly broader than initially anticipated. In January 2025 alone, over 1,089 unique IP addresses were observed attempting to exploit the vulnerability. In total, 79 distinct exploitation techniques have been documented, all capable of enabling remote code execution on vulnerable systems.
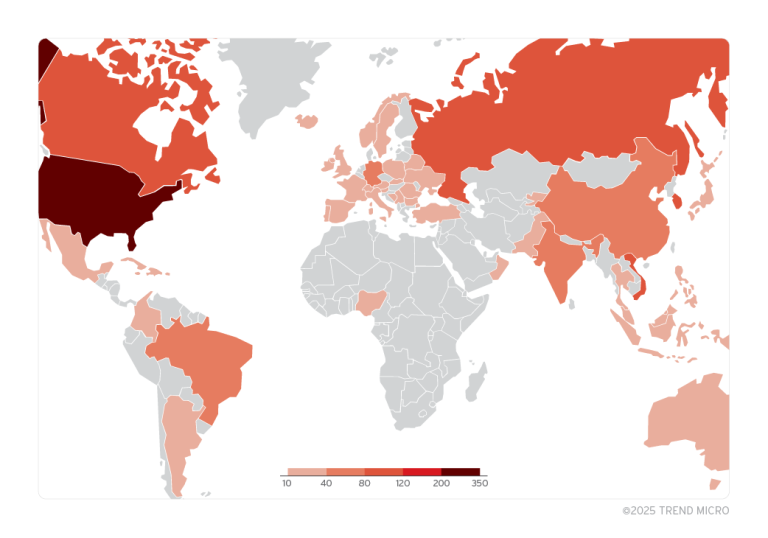
GreyNoise has confirmed that the attacks have now spread across multiple regions, including the United States, Singapore, the United Kingdom, Spain, and India, with a sharp rise in activity toward the end of January. Notably, over 43% of the malicious traffic has been traced back to Germany and China. February saw further spikes in exploitation attempts, indicating automated network scanning in search of vulnerable targets.
Although CVE-2024-4577 was discovered and patched in mid-2024, attacks have persisted unabated. The primary objective of the attackers appears to be credential theft and long-term persistence within compromised systems, facilitating follow-up intrusions. A notable attack in August 2024 targeted a university in Taiwan, suggesting that the threat had extended beyond Japan long before GreyNoise’s latest findings.
Security experts strongly urge organizations running Windows servers with exposed PHP-CGI to adhere to security best practices, conduct retrospective network activity analysis, swiftly block malicious IP addresses, and apply the latest security updates without delay.