Earth Preta’s kill chain | Source: Trend Micro
The Chinese cyber-espionage group Mustang Panda has adopted a novel technique to evade antivirus detection and maintain persistent control over compromised systems. Researchers at Trend Micro have uncovered that the attackers leverage a legitimate Windows utility, Microsoft Application Virtualization Injector (MAVInject.exe), to inject malicious code into the waitfor.exe process when an active ESET antivirus installation is detected on the target machine.
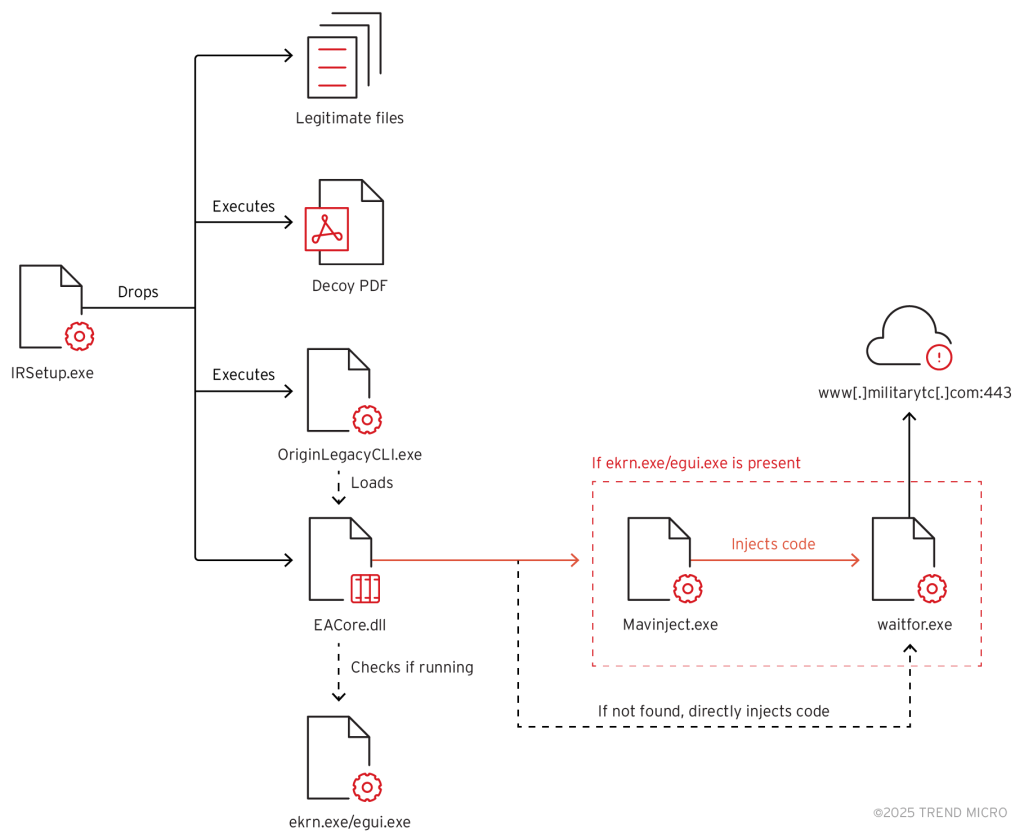
The attack sequence begins with the deployment of multiple files, including legitimate executables, malicious components, and a decoy PDF document designed to distract the victim. The adversaries employ Setup Factory, a Windows installer creation tool, to conceal their payload and facilitate stealthy execution.
The initial malicious file, IRSetup.exe, functions as a dropper, delivering multiple components to the system, including a lure document tailored for users in Thailand, suggesting the possible use of phishing emails as the primary infection vector.
Subsequently, the malware executes a legitimate Electronic Arts application (OriginLegacyCLI.exe) to load a rogue DLL (EACore.dll), a modified version of the TONESHELL backdoor, previously linked to Mustang Panda. The malware’s primary objective is to check for active ESET antivirus processes (ekrn.exe or egui.exe). If the security software is detected, the malware executes waitfor.exe and exploits MAVInject.exe to inject its payload in a manner that bypasses detection.
According to security analysts, MAVInject.exe allows attackers to inject malicious code into a running process while evading traditional antivirus defenses. It is likely that the hackers thoroughly tested the attack on systems equipped with ESET security solutions to ensure its effectiveness.
In the final stage of the attack, the malware decrypts an embedded shellcode, which establishes a connection with a remote command-and-control server. This grants the attackers the ability to upload and download files and initiate remote control over the compromised machine.
By leveraging legitimate Windows utilities, Mustang Panda continues to refine its attack methodologies, executing malicious payloads covertly. This strategic approach enables them to circumvent antivirus defenses and maintain long-term access to compromised systems with minimal risk of detection.