Online access to personal data begins with a seemingly simple step—entering a password. However, the widespread practice of reusing the same password across multiple services remains a critical security vulnerability, exposing users to significant risks. A recent analysis by Cloudflare revealed that 41% of all successful logins on websites protected by its security mechanisms were carried out using stolen credentials, highlighting the alarming scale of password reuse.
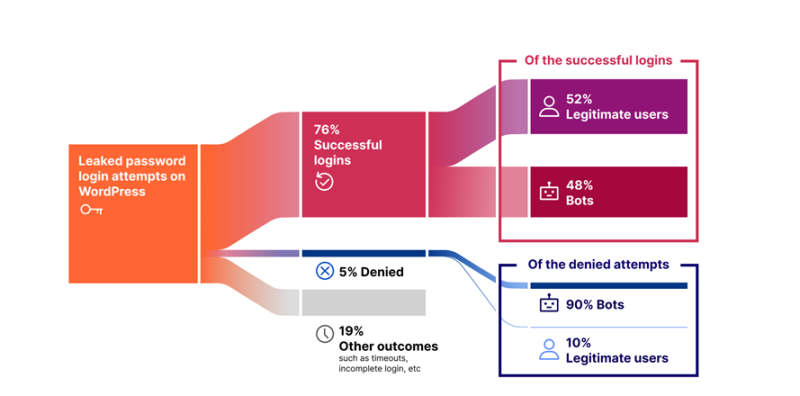
Between September and November 2024, cybersecurity specialists examined user and bot traffic, as well as the impact of data breaches on content management systems (CMS). Their findings indicated that leaked credentials not only endanger individual users but also compromise major platforms such as WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. Notably, 76% of login attempts using compromised credentials on WordPress sites were successful, with nearly half of them executed by automated bots.
Bots play a pivotal role in credential-stuffing attacks, an automated hacking technique where hundreds of thousands of stolen username-password combinations are systematically tested against various online services. These bots leverage breached data from repositories like Have I Been Pwned, making them exceptionally effective. According to Cloudflare, a staggering 95% of all login attempts using compromised credentials were performed by bots, reaffirming the persistent and evolving nature of automated cyber threats.
CMS platforms are particularly vulnerable to such attacks due to their reliance on standard authentication mechanisms that often lack robust protective measures. Even basic security enhancements, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or login attempt rate limiting, could significantly mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. However, statistics indicate that only 5% of login attempts with leaked passwords were successfully blocked, underscoring insufficient safeguards in place.
Despite increasing awareness of cybersecurity threats, password reuse remains a prevalent issue. A Forbes study found that, on average, users apply the same password across at least four different accounts. Consequently, when a breach occurs, attackers can gain access to multiple services linked to the victim’s compromised credentials, amplifying the security risk.
To defend against such threats, users should adopt unique, complex passwords for each account and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Website administrators, in turn, should implement compromised credential detection systems, enforce stricter login attempt limitations, and proactively enhance their security infrastructure to combat the escalating threat of automated cyberattacks.