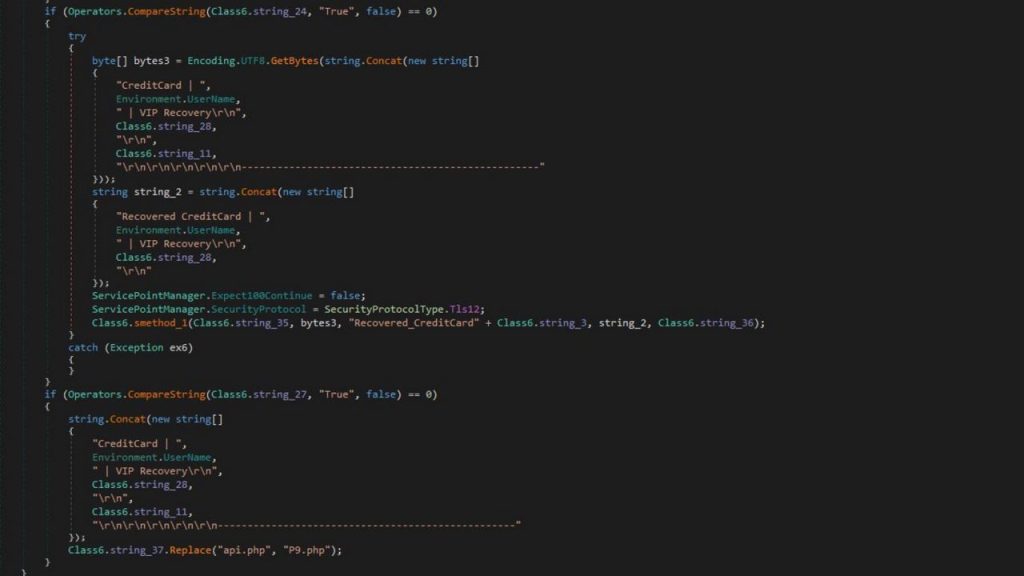
Snake Keylogger’s attempt to steal the victim’s credit card information
According to a report by Fortinet, a new variant of Snake Keylogger is targeting Windows users in Asia and Europe, employing an unconventional evasion technique. The malware now leverages the AutoIt scripting language to complicate detection by antivirus solutions.
Snake Keylogger is a .NET-based information stealer. As in previous versions, it infiltrates victims’ devices through malicious email attachments, logging keystrokes, capturing desktop screenshots, and extracting clipboard data. Consequently, cybercriminals gain access to victims’ accounts, banking credentials, and other sensitive information, including passwords stored in Chrome, Edge, and Firefox browsers.
The stolen data is exfiltrated to hacker-controlled servers via multiple channels, including SMTP, Telegram bots, and HTTP requests. Fortinet researchers have identified that the new variant is distributed as a compiled AutoIt binary, allowing cybercriminals to conceal the primary malicious payload within an executable file, thereby complicating analysis and detection.
AutoIt is a free scripting language designed for task automation in Windows and is commonly used to create standalone executable files. By exploiting this technology, threat actors gain a tool capable of circumventing traditional antivirus defenses.
Upon execution, the malware copies itself into the %Local_AppData%\supergroup directory under the guise of ageless.exe, effectively concealing its presence. To ensure persistence after a system reboot, the keylogger generates a VBS script, ageless.vbs, within the Windows startup folder. This approach enables Snake Keylogger to maintain control over the infected device even if the primary process is forcibly terminated by the user or security software.
Furthermore, the malware injects its malicious payload into the system process RegSvcs.exe using a process hollowing technique. This method allows attackers to replace code within a legitimate process, evading behavioral analysis and security mechanisms.
For keystroke interception, Snake Keylogger utilizes the SetWindowsHookEx API with the WH_KEYBOARD_LL parameter, granting it the ability to monitor all user input. Beyond keylogging, the malware also determines the victim’s geographic location via IP address by querying checkip.dyndns.org.
Fortinet analysts warn that the use of AutoIt significantly enhances the stealth capabilities of this Snake Keylogger variant, as it can masquerade as legitimate automation scripts and bypass conventional security measures. Users are strongly advised to refrain from opening email attachments from unknown senders and to keep their antivirus databases up to date.