In recent months, cybersecurity experts have observed a surge in hacker activity targeting unpatched vulnerabilities from 2022 and 2023 in inadequately secured systems. According to threat intelligence platform GreyNoise, a significant spike in attacks has been detected against CVE-2022-47945 and CVE-2023-49103, which affect the ThinkPHP framework and the ownCloud file service, respectively.
Both vulnerabilities are classified as critical, as their exploitation enables attackers to execute arbitrary commands on the operating system or exfiltrate sensitive data, including administrator passwords, mail server credentials, and software license keys.
CVE-2022-47945 is a Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability present in ThinkPHP versions prior to 6.0.14. The flaw stems from a language parameter that, when a language pack is enabled, can be leveraged for unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE).
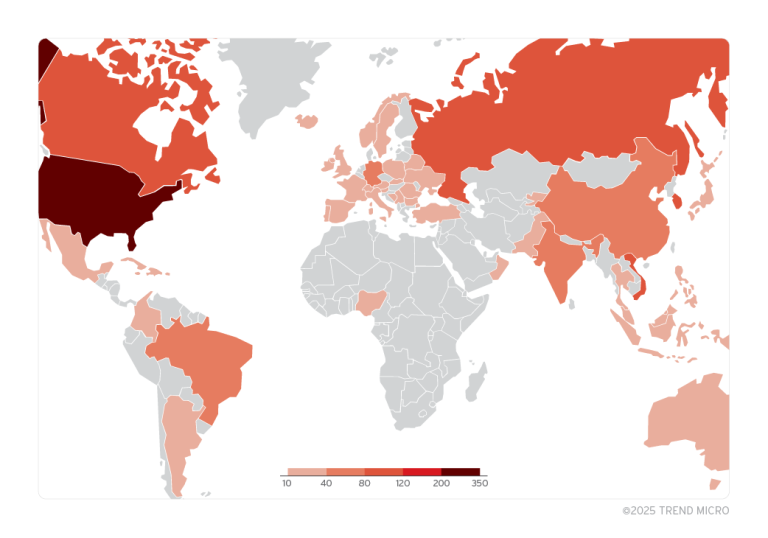
During the summer of 2024, security researchers at Akamai detected Chinese hacker groups exploiting this vulnerability, and since October 2023, attack activity has sharply escalated. As of now, GreyNoise has identified 572 unique IP addresses actively exploiting CVE-2022-47945.
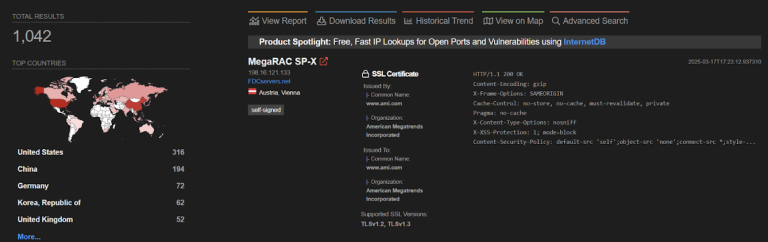
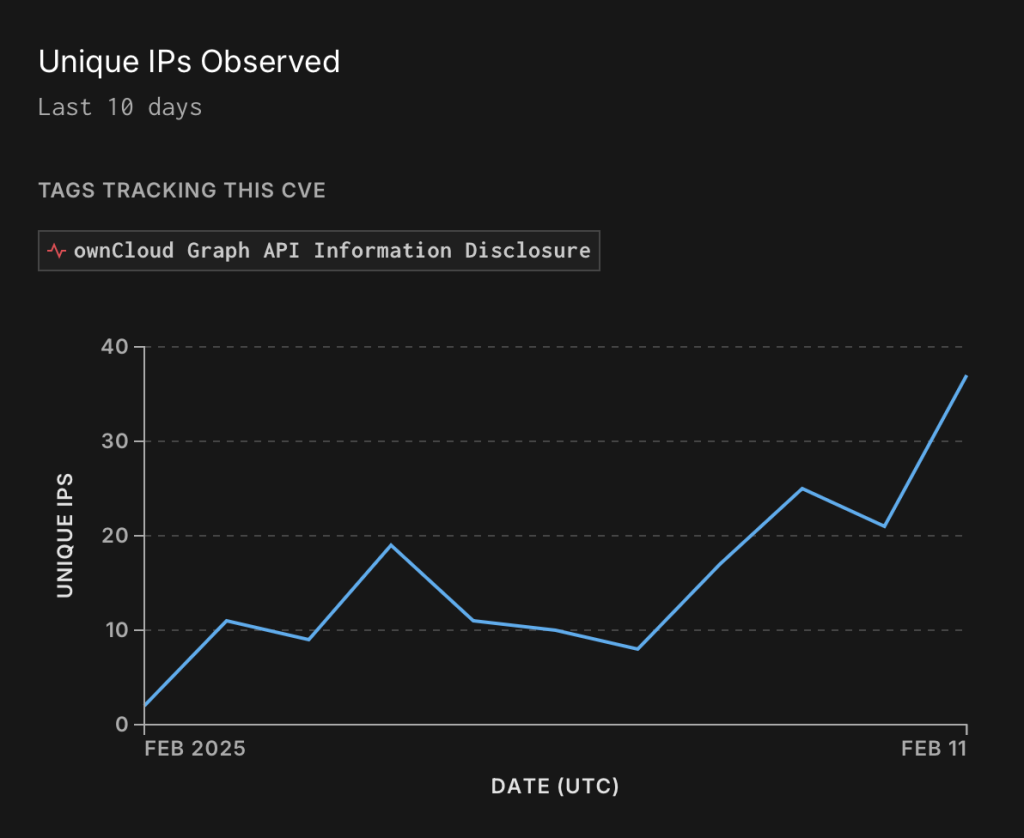
The second vulnerability, CVE-2023-49103, affects the ownCloud platform and originates from a flawed third-party library, which allows PHP environment variables to be extracted via URL manipulation. Following its disclosure in November 2023, threat actors swiftly began weaponizing the flaw to steal data from unprotected servers.
A year later, the vulnerability was listed among the 15 most exploited security flaws of 2023 by the FBI, CISA, and NSA. Despite a patch being released over two years ago, numerous systems remain unpatched and continue to be vulnerable to attacks.
According to GreyNoise, recent days have seen a surge in attacks on CVE-2023-49103, with the number of unique IP addresses involved now reaching 484.
Security professionals strongly urge administrators to upgrade ThinkPHP to version 6.0.14 or later and deploy GraphAPI 0.3.1 for ownCloud. Additionally, systems that may be vulnerable should be isolated from the network or placed behind a firewall to minimize the risk of successful exploitation.